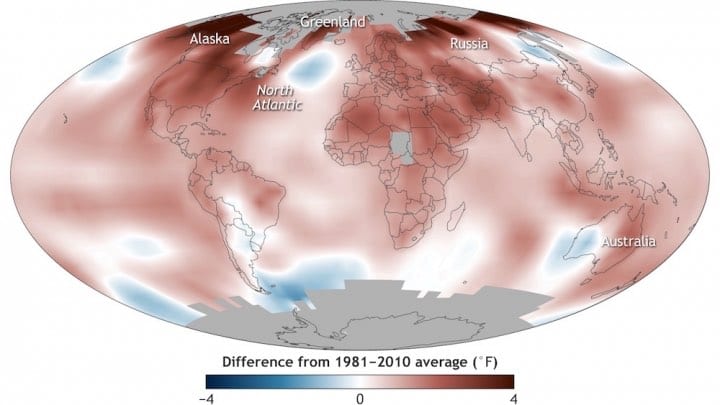
By now, we’ve all heard that 2016 was the hottest year on record, and that heat-trapping greenhouse gases hit their highest concentration ever, surpassing 400 parts per million for the first time in nearly 1 million years.

Credit: NOAA
But there are other climate change-related records that have flown more under the radar. Several of those records were highlighted Thursday in the annual State of the Climate report, released in the Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society:
For example, during August, ice-free areas of the Barents Sea (north of Norway and Russia) were up to 20°F (11°C) above average, a figure that stunned climate scientists.
The Chukchi Sea off Alaska and the waters to the west of Greenland were 13°F to 14°F above average. Those warm waters were linked to the smallest annual winter peak in sea ice levels and the second lowest annual minimum.
The average land surface temperature for the Arctic was 3.6°F (2.0°C) above the 1981-2010 average — a 6.3°F (3.5°C) rise in temperatures since 1900. Record-high temperatures were measured below the surface of the permafrost, or permanently frozen ground, across the North Slope of Alaska.

Credit: NOAA
“2016 was a year in the Arctic like we’ve never seen before,” Jeremy Mathis, director of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s Arctic research program and an author of the report, said.
The rate of warming in the Arctic, which is happening at twice the rate of the rest of the globe, has major impacts on local ecosystems, but also further drives the warming of the planet, as the sea ice that would reflect the sun’s rays back to space is lost.
And for the 37th consecutive year, alpine glaciers retreated across the globe. These glaciers are a major source of water for local communities, and their loss has led to concerns about water security, particularly in places like Southeast Asia.

Credit: NOAA
Source: Climate Central. Reproduced with permission.