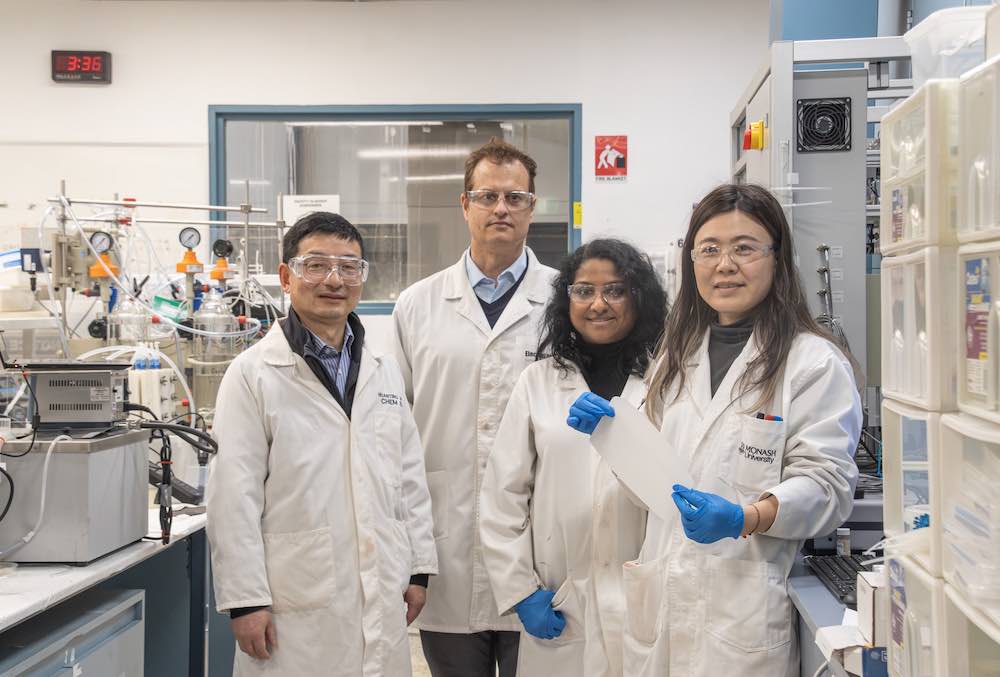
A start-up spun out of Monash University is developing technology that promises to dramatically increase the efficiency of lithium production, a critical mineral for battery technologies used in electric vehicles and renewable energy storage.
Based on research from world-renowned membrane expert Laureate Professor Huanting Wang of Monash University, ElectraLith’s technology offers a “cleaner, cheaper, faster” method of filtering lithium from salt lakes, mine tailings, and other brine solutions – including potential new sources.
The extraction method using ElectraLith’s novel membrane needs only small amounts of solar electricity and does not require added chemicals or water.
It is hoped that the technology could help to dramatically increase the efficiency of lithium production, to meet demand that, from the renewable energy sector alone, is projected to increase by up to 800% by 2050.
Compatible with renewable electricity and boasting the potential to reduce lithium production costs by up to 40%, ElectraLith’s innovative membrane technology offers the potential of making onshore processing more competitive with the lowest energy requirement and environmental impact of all approaches to lithium refining.
“Current lithium extraction methods involve either roasting hard rock at high temperature and dissolving it with hot sulfuric acid, or evaporating brines in a solar pond, both of which use chemicals to precipitate lithium out,” said Professor Huanting Wang, director of the ARC Research Hub for Energy-efficient Separation at Monash University.
“It is time consuming, disruptive, expensive, and wasteful.
“My research in nanostructure membranes is all about efficiency and ingenuity to make the most of this limited mineral resource,” Wang says.
Monash Engineering’s Dr Zhouyou (Emily) Wang recognised the potential of Professor Wang’s innovation and has subsequently awarded an Australian Research Council Early Career Industry Fellowship to further develop and commercialise the technology.
“Even though seawater is a brine, the concentration of Lithium is too low for cost effective extraction, but we are already thinking about designing the next generation of membranes to improve Lithium extraction, so maybe in the future we can extract Lithium from new sources,” said Dr Wang.